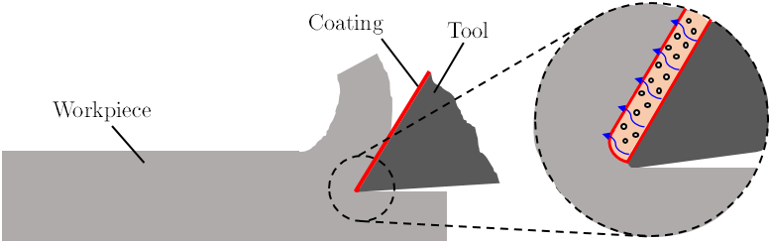
Increasing requirements on high-speed and dry cutting applications open up new demands on the quality of cutting tool materials. This is particularly important in the aerospace and automotive industries where easy and premature degradation of the cutting tools is observed during the machining of hard-to-difficult materials. Several solutions have been tried to improve the machinability of these alloys, being the application of thin solid films by sputtering techniques the most promising. However, so far, such a solution does not yet allow meet the need for high-speed machining and green manufacturing required for machining those materials.
Recently, a successful UT Austin Portugal exploratory project developed a new efficient green coating system with the capacity to control the release of a lubricious phase able to improve the cutting performance of hard-to-machine materials. The coatings, based on the TiSiN-Ag system, were deposited with a nanocomposite structure (nc-TiN grains imbibed in an a-Si3N4 phase) with Ag in the form of nanoclusters evenly distributed in the bulk. At high temperatures, due to Ag out-diffusion, the adhesion of the counterpart material to the coating is avoided with a significant decrease in the friction coefficient, preventing the growth of building edges which often leads to the cutting tool failure.

Relevant publications:
- Movchan, A. B., Rebrov, K. R., & Rodin, G. J. (2021). Axisymmetric deformation of compressible, nearly incompressible, and incompressible thin layers between two rigid surfaces. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 214, 61-73.
- Cavaleiro, D., Carvalho, S., Cavaleiro, A., & Fernandes, F. (2019). TiSiN (Ag) films deposited by HiPIMS working in DOMS mode: Effect of Ag content on structure, mechanical properties and thermal stability. Applied Surface Science, 478, 426-434.
