Architected Materials
Imagine repairing damage to your car by applying heat, or retrofitting buildings and bridges in hours instead of weeks, or deploying extraterrestrial habitats autonomously. These ideas may seem like science fiction, but are achievable with architected materials. Architected materials can exhibit extraordinary and unusual properties. These materials typically consist of periodic unit cells. By tailoring the features of the unit cells, we can enable novel properties like superelasticity, negative Poisson’s ratio, negative thermal expansion, and more. These special properties mean we can address grand challenges in civil engineering in new ways.
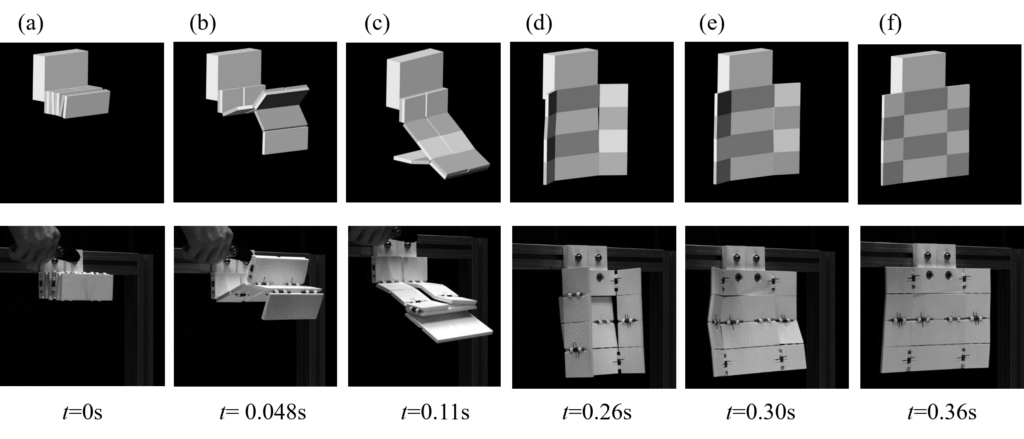
Advanced Structures
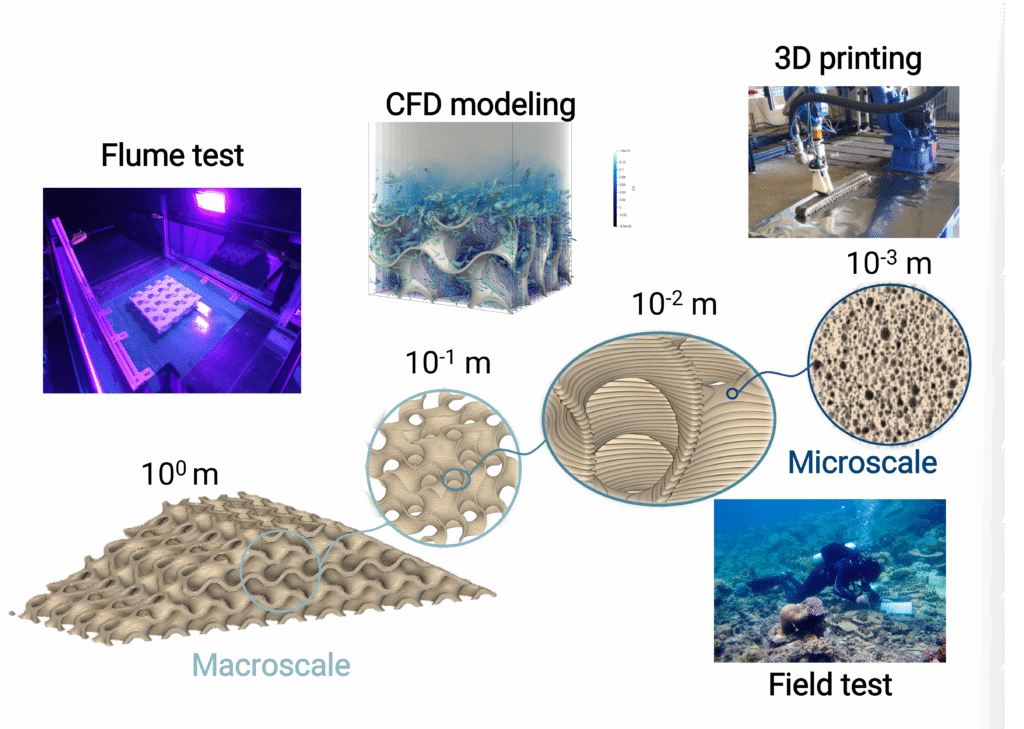
Nature-inspired Architected Coastal Resilient Ecostructures (NACRE)
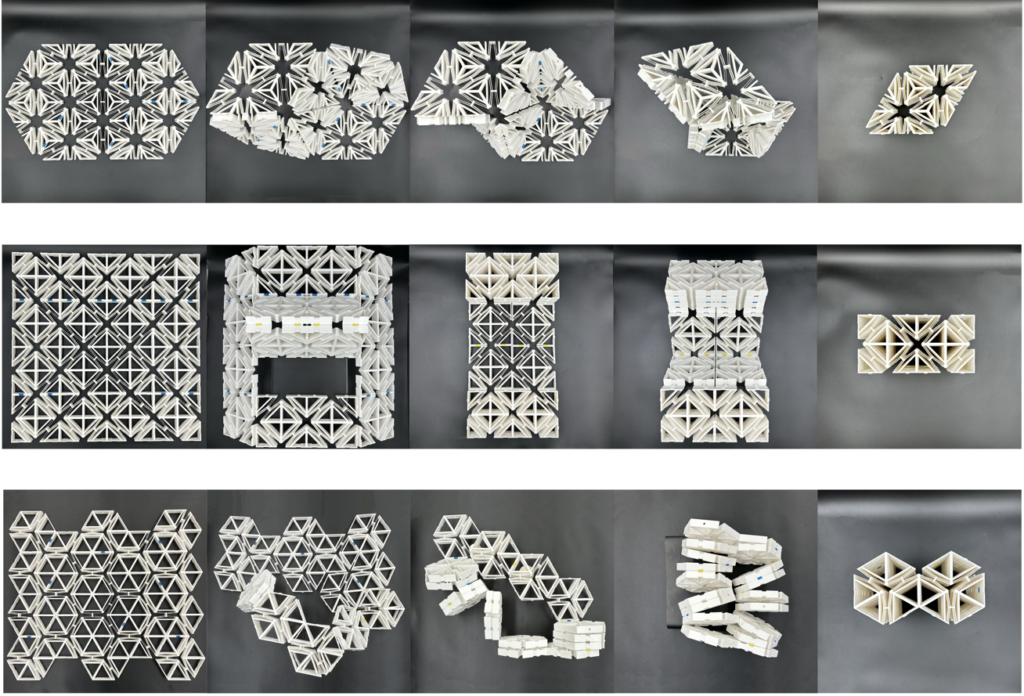
NACRE is a new class of multifunctional coastal infrastructure that integrates advanced manufacturing, architected materials, and ecological design to protect communities while restoring ecosystems. NACRE building blocks are modular, tunable, and adaptive, providing measurable wave energy reduction, habitat complexity for biodiversity, and repairability over time. Unlike conventional gray or green approaches, NACRE combines structural resilience, ecological enhancement, and community-driven design, offering a scalable and transformative pathway for coastal protection.
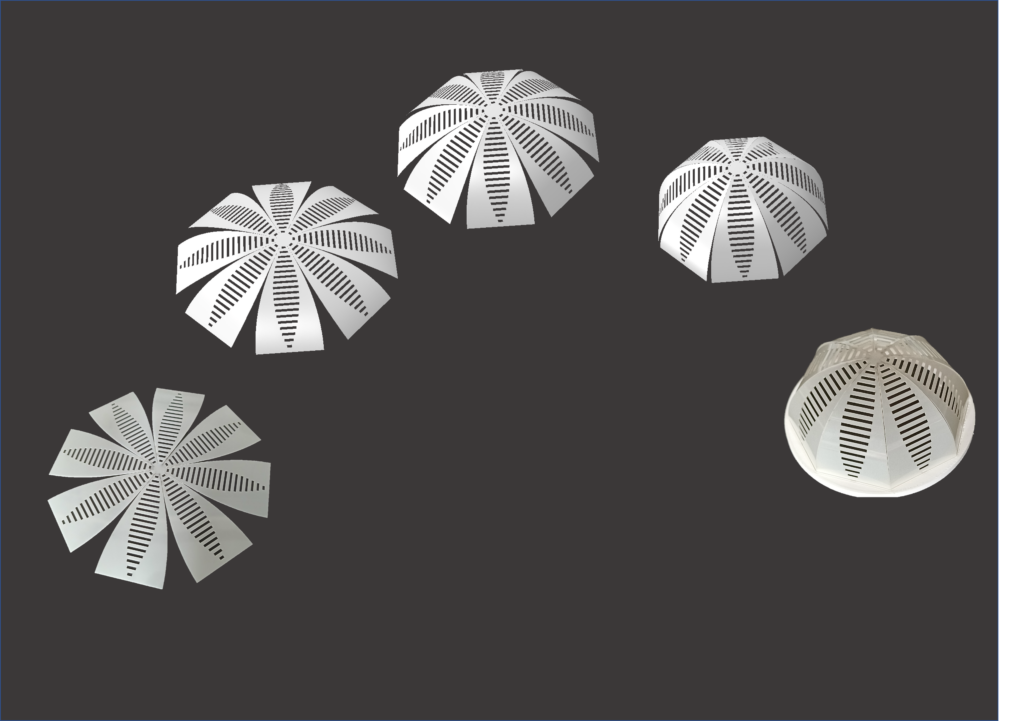
Shape Morphing Structures
Shape-morphing structures can change their shapes from one state to another. To form a desired 3D shape from a 2D sheet, we can employ the formalism of the ‘tapered elastica’ equation to design the customized 2D cut patterns and then generate the target 3D structure via small forces.
Deployable Structures
Deployable structures can be transformed from a compact configuration into a predesigned stable expanded form via an energy input. Applications of these structures range widely from medical devices to solar panels of spacecraft.