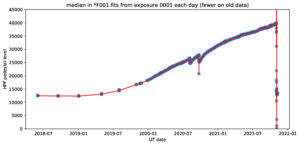
This past week the HPF instrument team has been working on the detector hardware. Over the past few years the bias/pedestal level has been slowly rising and recent exceeded 40k counts (of a total 65k available to the A/D converter). This high pedestal had begun impacting our ability to observe bright targets without saturation. The graph below shows the gradual rise of this pedestal level since 2019, and the rapid drop achieved this week during the detector maintenance. While the underlying cause of the pedestal rise is unknown, we anticipate that HPF will return to normal science observations in the coming days.
Category Archives: Instruments
VIRUS at 78
HPF searches for evaporating helium around young planets
HPF science updates
The Habitable zone Planet Finder continues advancing the field of exoplanets! See below for a round-up of recent updates:
Astronomers Disprove Planet Orbiting Nearby Barnard’s Star
https://mcdonaldobservatory.org/news/releases/20210518
A very stealthy alias: the impostor planet of Barnard’s star
https://hpf.psu.edu/2021/05/06/wavelength-dependent-behavior-of-the-hpf-fabry-perot/
HETDEX survey on track towards completion
This week there have been a few press releases from the HET partners about our progress on the HETDEX survey so far. The graphical presentation of the data is amazing and the whole survey will represent a major accomplishment for observational cosmology once completed. Read more at the following links below.
Meanwhile, our hearts are with the radio astronomy community as they mourn the not-unanticipated structural failure of the Arecibo radio telescope this week. Send warm thoughts to all the large aperture telescopes being maintained out there – they are are precious tools to view the cosmos and is is quite sad to lose such a giant.
https://mcdonaldobservatory.org/news/releases/20201201
https://news.psu.edu/story/640405/2020/12/01/research/hobby-eberly-telescope-dark-energy-experiment-survey-begins-full
https://phys.org/news/2020-12-hetdex-track-probe-dark-energy.html
Hazy skies overhead and HPF discovers the first warm Jupiter around an M dwarf
In the past couple weeks we’ve noticed significant (30-60%) reductions in the amount of starlight reaching the telescope, due to the smoke overhead:
https://hwp-viz.gsd.esrl.noaa.gov/smoke/index.html
It makes the sunsets eerie and washes out the Milky Way at night, too. Hopefully this situation will improve soon! The extinction seems worst at the blue wavelengths (like those that VIRUS uses) and is not bad for redder light (HPF observations are mostly unaffected).
On the brighter side, yet another HPF paper has been accepted and published – this one is the discovery and confirmation of the first transiting ‘warm’ Jupiter around an M dwarf. You can read the HPF team’s blog post about it:
https://hpf.psu.edu/2020/09/15/toi-1899/
The PSU press release:
https://science.psu.edu/news/Mahadevan9-2020
And of course the published article itself:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.07098
Hot Jupiters are rare around M dwarfs, and transiting warm Jupiters rarer still. The TESS spacecraft only detected a single transit – and it was only with HPF that we could nail down the orbital period and mass. This one definitely highlights the power of the HET and queue! Congrats to the whole team!
A Young Sub-Neptune-sized Planet Sheds Light onto How Planets Form and Evolve
Check out the latest results from the HET! There was a press release about this fascinating discovery:
https://mcdonaldobservatory.org/news/releases/20200804
For those who want the technical information, see the accepted article on the pre-print server: https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.12766
Another recent publication from HPF
New results from HPF: planets vs starspots!
The HPF team recently had another publication accepted describing the amazing complexities involved in separating star spots from planets. Their herculean efforts are described on this blog post and in their publication, both linked below:
https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2020arXiv200509657R/abstract
https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.09657
New results from HPF: helium detection in an exoplanet atmosphere
The HPF Team’s blog has a new post describing how they are characterizing an exoplanet’s atmospheric chemistry! It’s very cool stuff, available here: